A. PROJECT OVERVIEW
This project is supported by a grant of the Romanian National Authority for Scientific Research, CNDI– UEFISCDI, project number 55/ 2012.
Project Director
Florea Dinu
Dept. of Steel Structures and Structural Mechanics
Ioan Curea 1, 300224 Timisoara, Romania
Phone: +40 256 403 927
Abstract
The development of design guidelines for collapse control of the multi-story buildings started in 1968 with the collapse of the Ronan Point building due to a gas explosion. The failure of the building was identified as a "progressive collapse", because the extent of damage was disproportionate compared to the initial cause. Three decades later, in 2001, the attack against World Trade Center towers caused the complete failure of the two buildings and massive loss in lives and property. The type of collapse was again identified as progressive collapse. More recently, during the winter 2005/2006, several construction halls, shopping centers or hotels have been damaged or destroyed throughout Europe due to very heavy snowfalls. The concept of collapse control design can be considered the most appropriate approach for preventing the progressive collapse in case of extreme load events. In principle, the collapse control design method assesses and improves the redundancy of buildings by assuming the loss of structural members such as columns and beams due to extreme accidental loads and assessing how many members might be lost until the entire collapse of the building. The main objective of the project is the development of a performance based robustness design methodology for mitigation the progressive collapse of multi-story frame buildings against extreme load events, coming from both natural and man-made hazards. On this purpose, the research project will aim at definition, evaluation and modelling of the hazards, development of models for characterization of the material properties under different conditions, methods for structural evaluation and intervention strategies for mitigating the probability of collapse in case of extreme load events. All these subjects have a significant innovative character for actual state of knowledge and codification in Europe. As output, design criteria, numerical models, acceptance criteria.
Consortium
Coordinator (CO) – Politehnica University of Timisoara
Partner 1 (P1) - Technical University of Cluj-Napoca
Partner 2 (P2) - URBAN-INCERC (Cluj Branch)
Partner 3 (P3) - INSEMEX Petrosani
Partner 4 (P4) - SC ACI SA Cluj-Napoca
Objectives
The main objective of the project is the development of a performance based robustness design methodology for mitigation of progressive collapse of multi-story frame buildings against extreme load events coming from both natural and man-made hazards. The ability of the research team and each individual partner in conducting the research project and providing the anticipated outputs comes from the experience that has been gathered in previous work and their contribution to the state of the art. Partners involved in the project have brought many contributions to the relevant issues of the field. The outcome of their activity is reflected in scientific papers, national and international research projects and also dissemination of knowledge
B.ESTIMATED RESULTS
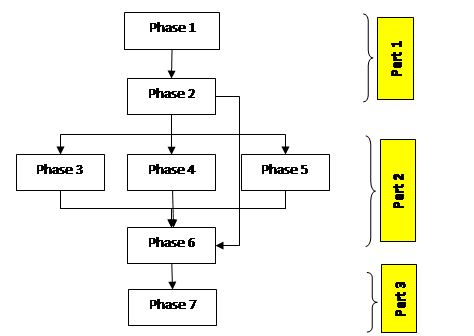
| Phase | Title | Deliverable |
| Phase 1 | Preliminary investigations | A Summary Report on progressive collapse and main causes |
| Phase 2 | Design of experimental and numerical program | Technical drawings, shop drawings and materials specifications for specimens |
| Phase 3 | Exp. Prog. on materials, welds details and macro-components | Test results on materials and weld details Test results on macro-components |
| Phase 4 | Experimental program on joints | Test results on beam-to-column joints and acceptance criteria for flexural and catenary response Test results in blast environment |
| Phase 5 | Experimental program on sub-assemblies | Test results on sub-assembly specimens |
| Phase 6 | Numerical program | Numerical models on test results Efficiency of collapse control design |
| Phase 7 | Design guidelines and recommendations | Synthesis of the results Guidelines for the collapse control performance based design of multi-story frame buildings against accidental actions Recommendations for best practice |
C. PARTNERS
The consortium involves five partners: four research institutions (two technical universities and two national institutes) and one major construction company.
D. PROJECT PROCESS
| Phase no. | Phase title | Status |
| 1 | Preliminary investigations | Completed |
| 2 | Design of experimental program and numerical program | Completed |
| 3 | Experimental program on materials, weld details and macro-components | Completed |
| 4 | Experimental program on joints | Completed |
| 5 | Experimental program on sub-assemblies | Completed |
| 6 | Numerical program | Completed |
| 7 | Design guidelines and recommendations | Completed |
Phase: Preliminary investigationsObjectives
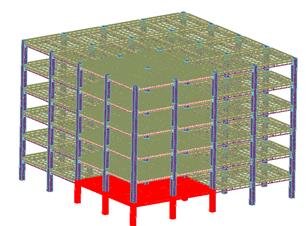
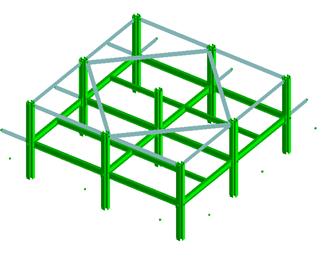
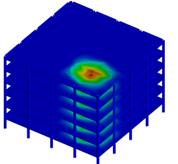
Task 1-1: Review of existing methods, identification of research needs The activity is devoted to a review of research on progressive collapse, related guidelines and recommendations as well as to the gaps in knowledge and research needs following the latest developments in the field. Case studies that can offer some insight into the problems of progressive collapse and lessons to be learned are also investigated. The benefits of seismic design philosophy on the integrity of the multi-storey structures will be identified. Task 1-2: Preliminary analysis and selection of case study structures In order to test realistic specimens, they are selected from representative multi-story frame structures, designed according to present code provision but without considering any accidental actions or loss of any element. Moment frames and braced frames are considered, with one way or two way behaviour, and with or without composite floors. Note that two-way structural framing systems have greater robustness than structures that are designed to span one way. The response can be improved also by using a two-way floor slabs, by adding supplementary ties or by allowing the gravity beams (along the simple spans) to develop the catenary behaviour. Deliverable: A Summary Report: the report describes the present development in the field of progressive collapse and causes of abnormal loading, underlines the gaps and research needs. The main directions of the research are indicated. (link doc 4.1) |
|
Phase: Design of experimental and numerical programObjectives
Task 2-1: Design of specimens for experimental program The experimental program consist of test on:
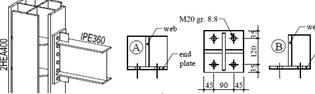
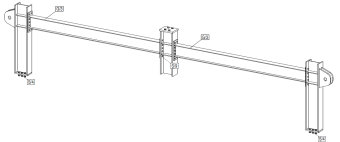
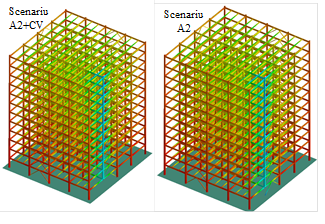
The largest specimens are the sub-assembly structures and are two-bay two-span models. Their dimension is 12m x 12m x 2m. Therefore, due to the limitation in the testing capacity of the host institution, the subassemblies specimens are half-scaled to cover two-bay two-span configuration. Similar tests are not available in the literature. Beam-to-column joints are tested under monotonic load beyond the flexural capacity to initiate the catenary behaviour. Similar tests have not been performed and are of great interest for column loss scenarios, where the verticals deflections can be large enough to develop the catenary tension. Connections must be capable of transferring catenary tension from beam to beam across the column. Different weld details are of concern, i.e. fillet welds, bevel butt welds. Strain rate from cvasi-static to dynamic range are of concern. Both the strength of steel and concrete increases significantly when the strain rate increases. The high strain rate might affect the ductility and failure mode of materials and welds. There is a large amount of specimens to be produced and supplied for testing program, as follows:
The supplier will be selected so as to assure a good quality of materials. In order to guarantee constant quality parameters, the fabrication of all steel specimens will be ordered to the same steelwork shop, with good expertise in the field. For the composite floors of the sub-assembly test, the concrete will be poured in the laboratory. Task 2-2: Design of numerical program The structures are designed to resist moderate and severe seismic actions. Different column loss scenarios are considered. Next figure shows the geometry of the reference frames. Sub-assembly and beam-to-column joint specimens will be selected from the reference structures and tested experimentally. The details are given in Phase 4 and Phase 5. Deliverables: Technical drawings, shop drawings and materials sspecifications for specimens: design of subassembly and beam-to-column joints, design of macro-component (T-stub), weld details and material specimens (main geometric dimensions, size and type of cross sections, connections, quality of materials, weld details and base material specimens), fabrication drawings and list of materials), as well as the testing rigs and set-up in laboratory. |
|
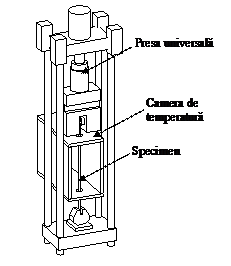
Experimental program (Phase 3, 4 and 5)- Task 3-1: Experimental test on base materials and weld details The mechanical properties of materials and the performance of the welds are important for the capacity of structural members to resist extreme load events. Tensile test at room temperature and toughness test at room temperature (20° C) and elevated temperature (540° C), under cvasistatic (0.05 mm/sec) and dynamic loading (10mm/sec) are performed. Impact, blast and explosions ask for high toughness of base material and welds in those members and connection components where a ductile response is expected. The weld details are loaded under monotonic loading.
|



 |
||||
|
- Task 3-2: Experimental test on T-stub macro-components The most important macro-components of bolted end plate beam-to-column connections are the T-stubs. The behaviour of such macro-components depends on the material characteristics, bolt arrangement and type of loading. The design of T-stubs for a ductile failure mode (see EN 1993-1-8) is based on a monotonic loading. The ductile failure mode can be altered in case of a dynamic loading (strain rate effect) or in case of fire (elevated temperature). In addition, the catenary action of beams can only develop if the connections have the capacity to sustain the tensile capacity of the beam. In order to evaluate the influence of parameters presented before, T-stubs are tested at room (20° C) and elevated temperature (540° C), under cvasistatic (0.05 mm/sec) and dynamic loading (10mm/sec).
Deliverables: Test results |


 |
|
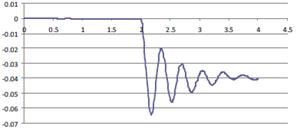
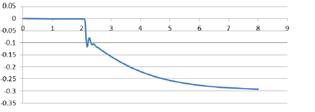
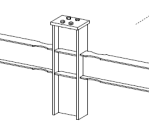
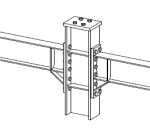
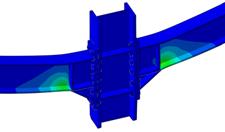
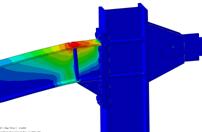
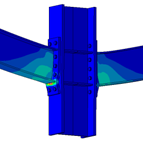
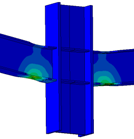
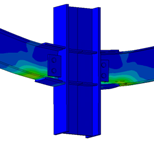
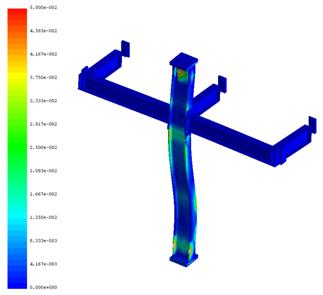
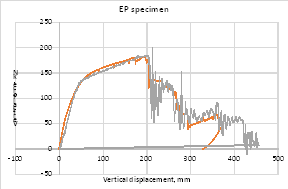
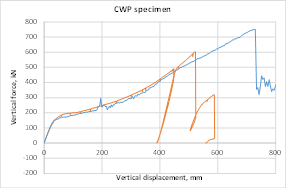
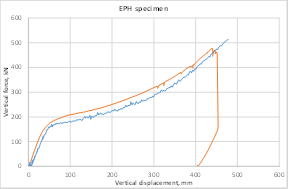
Experimental program (Phase 4 and 5) - Experimental test on joint specimens Pure beam-to-column steel joints are tested experimentally until the plastic rotation capacity is attained and further until the catenary action develops. Bolted and welded joints, full strength and partial strength are selected (80% of the beam capacity). The tests consist of pushing the middle column down until the failure of the specimen (push-down test) by means of hydraulic actuators. Numerical studies are in progress to evaluate the behaviour and key parameters (yielding, rotation capacity, ultimate capacity, total deformation capacity).
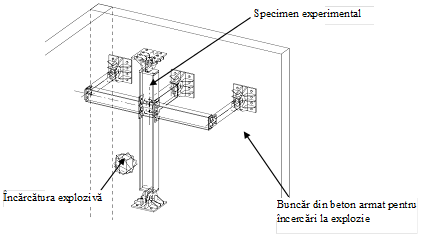
- Testing in blast conditions In this task, the blast effect on the beam-to-column components is investigated. The steel framing consists of a column and girder stud. Two types of girder stud to column connections, one rigid and one pinned are tested. The response modes and material behavior (fracture) is much different in a blast environment. Moreover, the stand-off distance is important and affects the behaviour. Therefore, different charges at different distances will be performed.
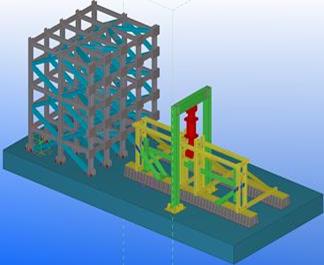
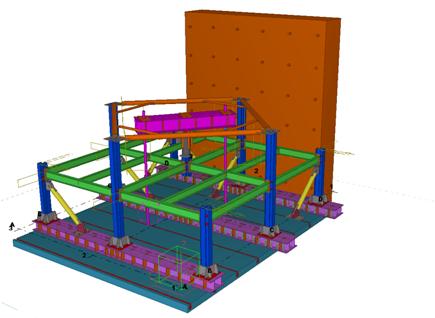
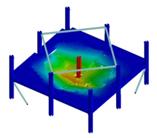
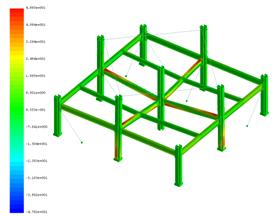
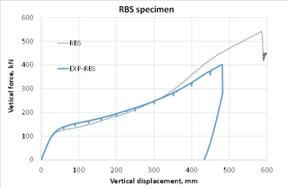
- Experimental test on subassembly specimens These tests simulate the response of an 3D assembly following a column loss. By using the membrane (catenary) effect of the floor structure or the bridging effect of the frame, the load of the lost column can be transferred to the adjacent members. The test specimens are half-scaled of a typical floor structure. The specimen is a two-bay two-span structure, with the size of 6.0x6.0x1.5m. Two solutions are tested: with and without concrete slab and two different scenarios are considered: middle column and corner column loss. The tests consist of pushing the column by imposing a vertical displacement with hydraulic actuators until the failure of the specimen (push-down test).
|
|
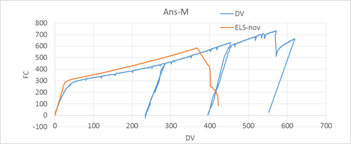
Phase 6 -Numerical programTask 6-1: Calibration and validation of numerical models based on test results The output of Phase 3, 4 and 5 serve as input for Phase 6. Models for materials and accidental actions, acceptance criteria and relevant limit states for different damage levels are used to calibrate the numerical models.
|
|
Phase 7 - Design guidelines and recommendationsObjectives
Task 7-1: Guidelines for the collapse control performance based design of multi-story frame buildings against accidental actions Designers would benefit from a standardized procedure in order to ensure general structural integrity of multi-story frame buildings. The method can be used for design of new buildings and for the upgrading of the existing ones. A performance matrix for robustness base design will be also provided. Task 7-2: Recommendations for best practice in selection of structural system, fabrication and material requirements for improving the robustness Ensuring the structural integrity of new buildings may be provided by following prescriptive minimum requirements for design. This includes minimum requirements for connections, tie force resistance, continuity and ductility. This can be used for low level of consequence buildings (protection). |
|
E. PUBLICATIONS
Conference articles:
Journals:
Experimental testing and numerical analysis of 3D steel frame system under column loss, Engineering Structures, Volume 113, 15 April 2016, p 59-70, ISSN 0141-0296, (https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2016.01.022)
Improving the structural robustness of multi-story steel-frame buildings, Structure and Infrastructure Engineering. Maintenance, Management, Life-Cycle Design and Performance, - Volume 11 (2015), Number 8, p. 1028-1041-(http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/15732479.2014.927509)
Structural Connections of Steel Building Frames under Extreme Loading, Advanced Materials Research Vol 1111 (2015) pp 223-228, (doi:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.1111.223)
Project presentation:
Nordic Steel Conference, 5-7 September, Oslo, Norway
Master and PhD theses:
Robustness of moment steel frames under column loss scenarios
Ultimate deformation and resistance capacity of bolted T-stub connections under different loading conditions (http://www.ct.upt.ro/suscos/files/2015-2017/Ghazanfar%20Ali%20ANWAR_Dissertation.pdf) --- Dissertation developed in the framework of Sustainable Constructions under natural hazards and catastrophic events European Erasmus Mundus Master Course (http://steel.fsv.cvut.cz/suscos/index.htm )
Response of T-stub macro components under high speed loading caused by column loss
Membrane action of slabs in framed structures in case of accidental column loss (http://www.ct.upt.ro/suscos/files/2012-2014/Kovecsi_dissertation.pdf) --- Dissertation developed in the framework of Sustainable Constructions under natural hazards and catastrophic events European Erasmus Mundus Master Course (link http://steel.fsv.cvut.cz/suscos/index.htm )
Behaviour of beam-to-column joints under large vertical displacements following the loss of a column (link http://www.ct.upt.ro/suscos/files/2012-2014/Zdenek_dissertation.pdf ) --- Dissertation developed in the framework of Sustainable Constructions under natural hazards and catastrophic events European Erasmus Mundus Master Course (link http://steel.fsv.cvut.cz/suscos/index.htm )
Experimental tests on beam-to-column connections under column loss scenarios
Progressive collapse resistance of seismic resistant frames in case of column loss
Thematic Grant Research Proposals:
- Project title: "COLLAPSE PREVENTION DESIGN OF STORAGE RACK STRUCTURES", RFCS-2014 proposal, partners: Universitatea Politehnica din Timisoara (RO), Universite de Liege (BE), National Technical University of Athens – NTUA (GR), Universita degli Studi di Trento (IT), Bureau d'Etudes Greisch Societe Interprofessionnelle d'Ingenieurs et d'Architecture (BE), SC Dexion Storage Solutions SRL (RO)
- Project title: "Integrated approach for Collapse Control Design of Multistory Steel Structures under multi-hazard events", RFCS/FP7 proposal, partners: Imperial College (UK), University of Coimbra (Portugalia), University of Naples “Federico II” (Italia), Universitatea "Politehnica" din Timisoara, The Steel Construction Institute (UK), ARUP (UK), TATA Steel (UK).
- Project title: "Performant explosive charge for the fast cutting of metal structure.", propunere Parteneriate-PCCA 2013, Coordinator: INCD INSEMEX Petroșani; Partners: ISIM Timișoara, CN ROMARM Filiala SC Uzina de Produse Speciale Dragomirești SRL
E. LINKS
UEFISCDI — Executive Agency for Higher Education, Research, Development and Innovation Funding
ESF — European science foundation
ECCS — European Convention for Constructional Steelwork
WBDG - Whole Building Design Guide
FEMA — Federal Emergency Management Agency
NIST — National Institute of Standards and Technology